10 Common Causes of Hydraulic Equipment Failure
Hydraulic systems use pressurized fluid to convert mechanical energy into mechanical movement. These systems can be sensitive to outside factors that can cause the machinery to fail. Finding the source of these problems can be tricky because it could be a host of issues. Become familiar with the common causes of hydraulic equipment failure so you can find the right solutions to get your equipment back up and running.
Inadequate Fluid Levels or Incorrect Fluid Usage
One of the most overlooked aspects of hydraulic system maintenance is proper fluid levels. Hydraulic fluid is essential for transmitting power, lubricating components, and keeping the system cool. When fluid levels drop below the recommended levels, the system can become inefficient, leading to increased wear and potential damage. Regularly checking and maintaining the correct fluid levels should be a standard part of every maintenance routine.
Equally important is using the correct type of hydraulic fluid. Different systems may require specific fluids based on their operating environments and performance demands. Using the wrong fluid can lead to decreased efficiency, corrosion, and system failure. Always consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or a hydraulic equipment supplier to ensure you’re using the appropriate fluid for your system.
Persistent Fluid Leaks
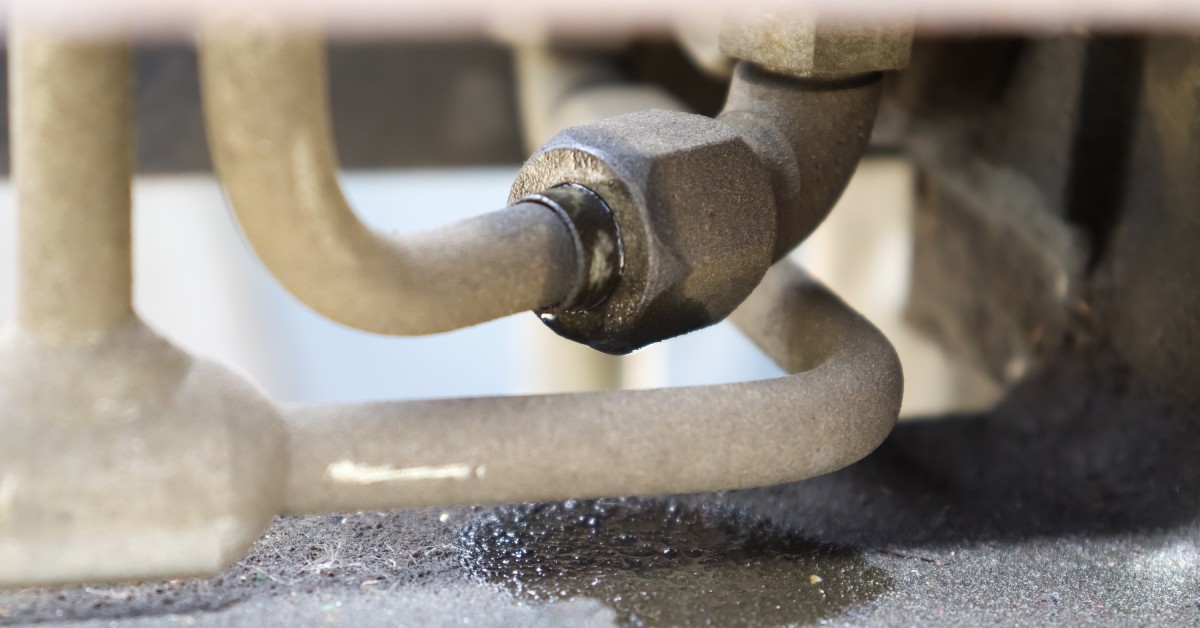

Leaks are another frequent issue that can significantly impact hydraulic systems. Even minor leaks can lead to a loss of pressure, reduced efficiency, and increased operating costs. Worn seals, loose fittings, or damaged hoses often cause persistent fluid leaks. Addressing leaks promptly is crucial to maintaining system integrity and performance.
Ignoring leaks can lead to a cascade of problems, including contamination and overheating. Regular inspections of hoses, seals, and connections can help identify and rectify leaks before they escalate. Incorporating leak detection into routine maintenance practices ensures that minor issues don’t become major headaches.
Contamination Intrusion
Contamination is a silent adversary in hydraulic systems. Particles like dirt, metal shavings, and other debris can infiltrate the system through various means, including improperly sealed components or contaminated fluid. Once inside, these particles can cause significant wear and tear on components, leading to premature failure.
Preventing contamination starts with implementing rigorous cleanliness protocols. This includes cleaning all components before installation, using high-quality filters, and changing filters regularly.
Air Entrapment
Air entrapment is a common yet often overlooked issue in hydraulic systems. When air becomes trapped in the fluid, it can lead to erratic operation, increased noise, and reduced system efficiency. Air can enter the system through leaks, improper fluid filling, or faulty seals, so you must address any potential entry points.
The presence of air bubbles can also lead to cavitation, where vapor bubbles implode under pressure, causing damage to system components. Properly bleeding the system to remove trapped air is a straightforward maintenance task that can prevent these issues.
Corrosion Effects

Corrosion is often a hidden cause of hydraulic equipment failure. When metal parts are exposed to moisture and other corrosive elements, they oxidize and degrade over time. This can lead to compromised seals, damaged parts, and reduced performance. Corrosion affects the integrity of components and allows contaminants to enter the system, causing more damage.
Regular maintenance and monitoring can help combat corrosion. Applying anti-corrosion treatments or coatings can also reduce the risk of damage. Additionally, controlling factors like temperature and humidity and ensuring hydraulic fluid is free from water impurities are vital to prevent failures.
System Overheating
Overheating is a prevalent cause of hydraulic equipment failure, often resulting from inadequate cooling, excessive load, or fluid contamination. High temperatures can degrade seals, reduce fluid viscosity, and lead to component fatigue. Monitoring system temperature and implementing effective cooling solutions are vital to maintaining optimal performance.
To prevent overheating, check that cooling systems are functioning correctly and free from obstructions. Regularly monitor fluid temperature, and replace it if it becomes discolored or loses its lubricating properties. Addressing overheating extends the life of the system.
Overloading the System
Hydraulic systems are designed to handle specific loads, and exceeding these limits can lead to severe consequences. Overloading can cause excessive pressure and stress on components, resulting in wear, damage, and, ultimately, failure. Operators must adhere to manufacturer specifications and avoid pushing the system beyond its capabilities.
Educating equipment operators about load limits and implementing safeguards can help prevent overloading. By understanding the system’s limitations and operating within them, you can maintain performance and avoid unnecessary downtime and repairs.
Component Wear and Deterioration
All mechanical systems experience wear and tear over time, and hydraulic systems are no exception. Key components such as pumps, valves, and hoses can deteriorate due to continuous use, leading to decreased efficiency and potential failure. Regularly inspecting and replacing worn components is a crucial aspect of preventive maintenance.
Recognizing the signs of wear, such as reduced performance or unusual noises, can help identify components that need attention. By proactively addressing wear and deterioration, maintenance teams can keep systems running smoothly and prevent unexpected failures.
Neglected Maintenance
Neglecting routine maintenance is a surefire way to accelerate hydraulic equipment failure. Regular servicing can help you identify issues before they escalate into significant problems. Establishing a maintenance schedule and adhering to it ensures that systems remain in peak condition.
Maintenance should include checking fluid levels, inspecting for leaks, and monitoring system performance. A well-maintained system is less prone to unexpected breakdowns, saving time and resources in the long run.
Human Error
Human error is an unavoidable factor in any industry, including those using hydraulic equipment. Mistakes can occur during installation, operation, or maintenance, leading to system inefficiencies or failures. Training personnel and establishing clear procedures minimize the risk of human error.
Regular training sessions and clear communication can empower operators and technicians to perform their tasks accurately. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and attention to detail, organizations can reduce the likelihood of errors.
Understanding the common causes of hydraulic equipment failure is fundamental for anyone involved in maintaining and operating these systems. At Hyspeco, we understand that various factors contribute to smooth and efficient operation. Whether you’re looking for hydraulic training, engineering, or in-house fabrication, we offer a range of hydraulic services to help you combat hydraulic equipment failure. By addressing challenges head-on and implementing proactive maintenance strategies, you can extend your equipment lifespans, reduce downtime, and achieve greater operational success.

